Gynecomastia Correction
Gynecomastia Correction: Restoring a Natural Chest Contour
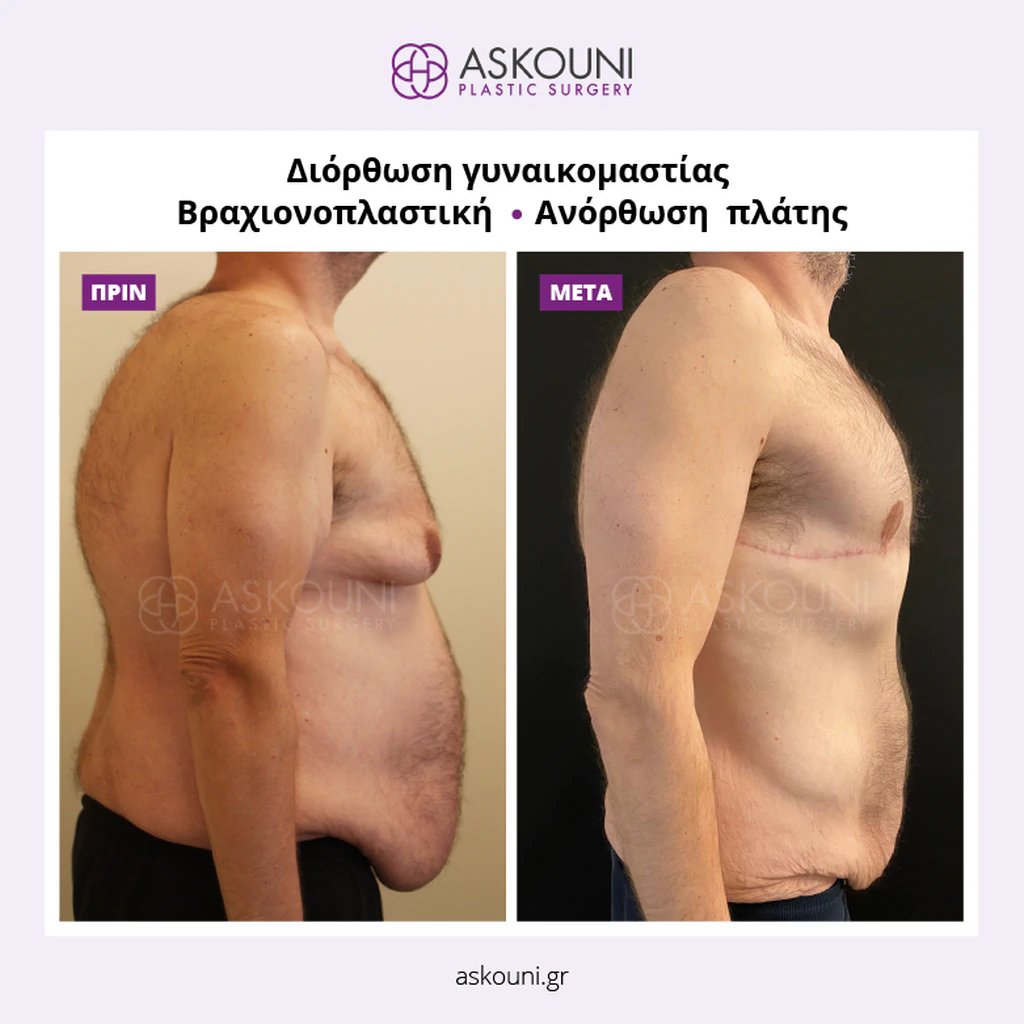
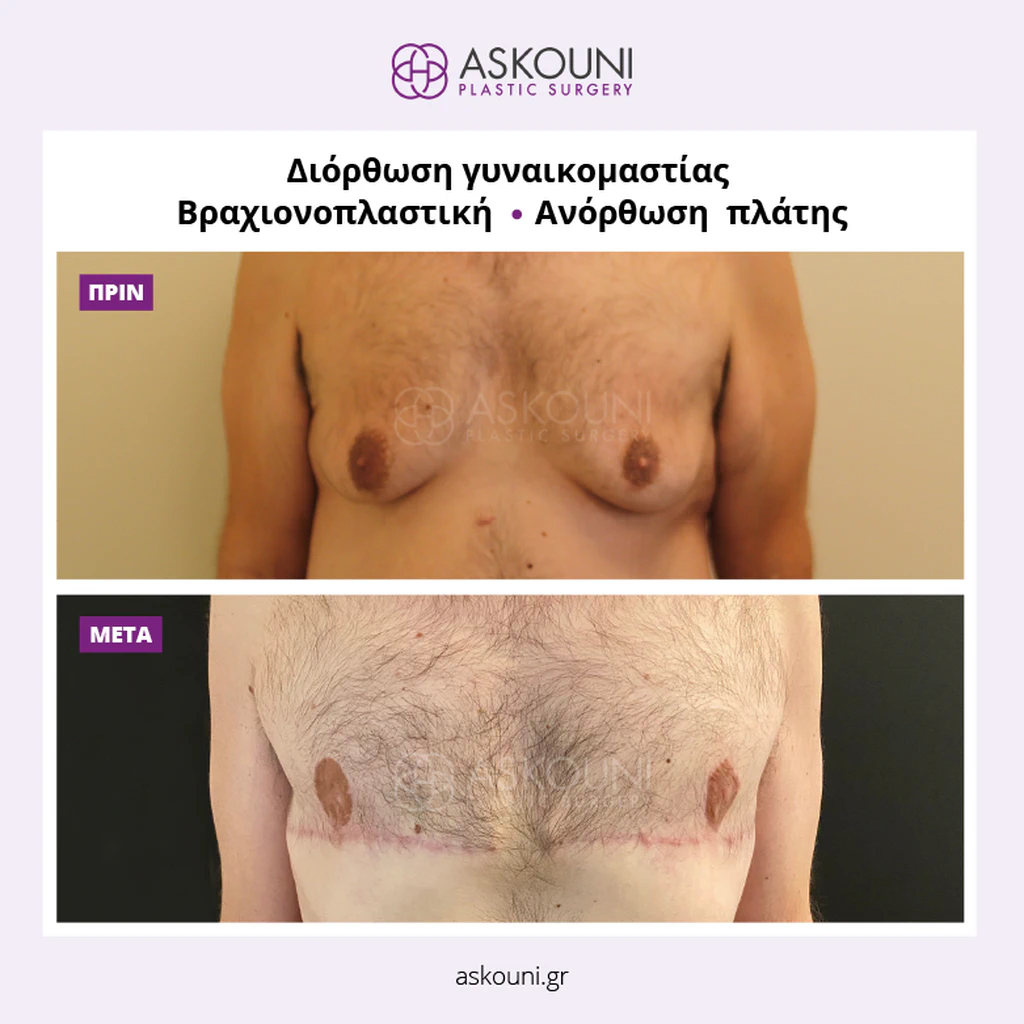
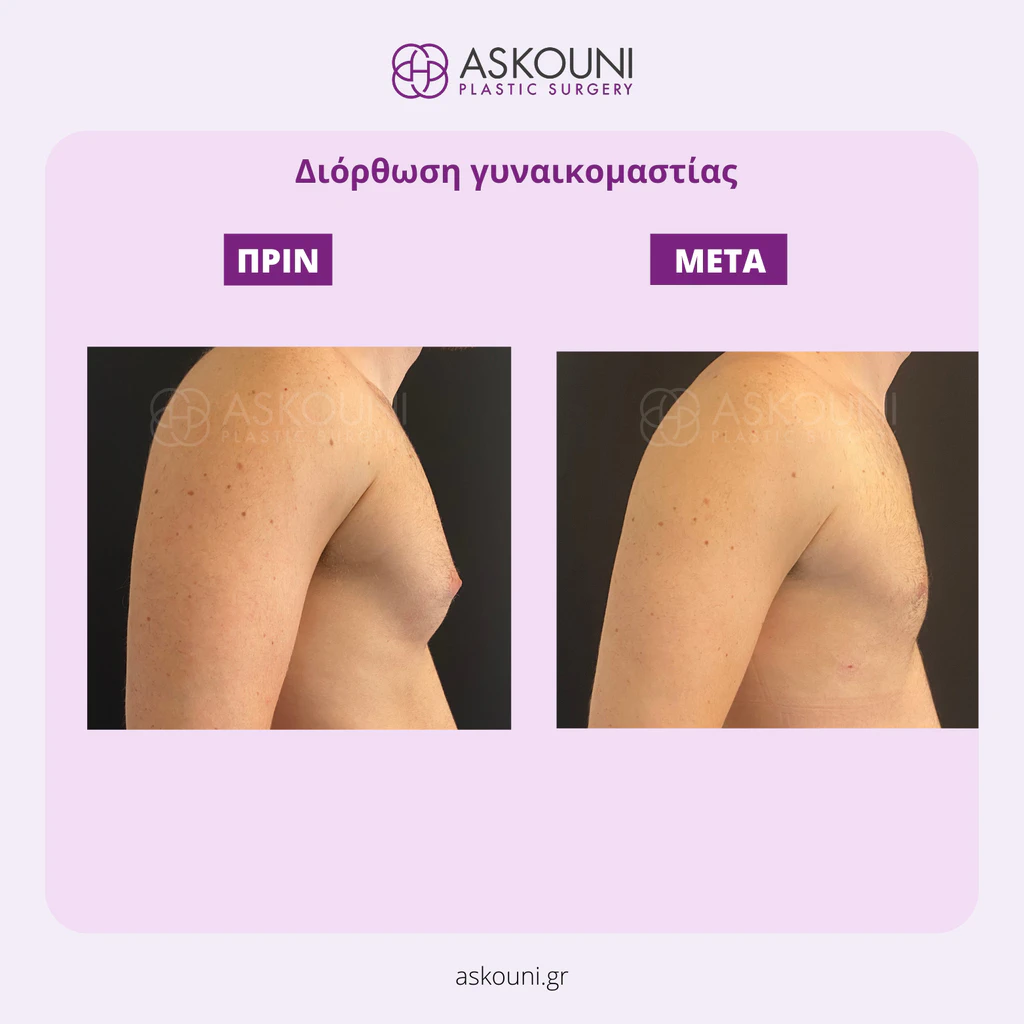
Gynecomastia is the benign proliferation of glandular tissue in the male breast, often creating a feminized chest contour. While physically harmless, this excessive development of the glandular parenchyma or adipose tissue can persist despite diet or exercise. Surgical correction, or male breast reduction, is a reconstructive procedure designed to remove this tissue and skin, restoring a flatter, firmer, and more masculine aesthetic. The approach is highly individualized, targeting specific anatomical layers to ensure a natural result.
Gynecomastia correction is indicated for men who experience persistent enlargement of the breast area that cannot be improved through medical treatment or weight optimisation. The consultation focuses on understanding the degree of tissue enlargement, its composition, and the quality of the overlying skin, as these factors directly influence the surgical plan and potential outcomes.
Candidate Suitability
Gynecomastia correction is indicated for men who experience persistent enlargement of the breast area that cannot be improved through medical treatment or weight optimisation. The consultation focuses on understanding the degree of tissue enlargement, its composition, and the quality of the overlying skin, as these factors directly influence the surgical plan and potential outcomes.
Typical candidates include those who:
- Show firm or glandular tissue beneath the nipple–areolar complex that does not reduce with exercise or dietary adjustments.
- Have excess fatty tissue localised to the chest, creating a visible fullness or asymmetry.
- Maintain a stable body weight, ensuring that postoperative contouring results are long-lasting and predictable.
- May experience discomfort or self-consciousness from clothing fit or physical activity due to the increased chest volume, prompting an interest in surgical correction.
Procedure Options and Techniques
The surgical strategy depends on the ratio of fibrous glandular tissue to adipose tissue. A Plastic Surgeon typically uses a combination of techniques:
- Liposuction: For enlargement primarily due to fatty tissue, liposuction techniques remove fat and sculpt pectoral definition.
- Surgical Excision: Used for dense glandular tissue or excess skin, involving an en bloc resection typically through an areolar incision.
- Combined Approach: Often, liposuction is performed in conjunction with excision to remove the gland and feather the edges for a smooth contour.
- Skin Resection: For significant sagging, excess skin may be excised to tighten the chest and reposition the nipple-areola complex to an anatomical position.
While rare, surgical interventions carry inherent risks. Potential issues include post-operative hematoma or seroma (fluid collections requiring drainage), temporary changes in nipple sensation, or slight asymmetry, though protocols minimize these occurrences.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery is critical for the longevity of the aesthetic result. Patients follow specific protocols to support tissue adherence:
- Compression Garments: A specialized compression vest must be worn to minimize edema and support retracting skin.
- Activity Restrictions: Light mobility is encouraged, but strenuous upper body exercise and heavy lifting are avoided for four weeks.
- Wound Management: Incision sites must be kept clean and dry, with the healing of the incision lines monitored to minimize scarring.
- Return to Routine: Most return to non-physical daily activities within a week, with residual swelling resolving over time to reveal the final definition.
Gynecomastia correction offers a well-established surgical approach for men seeking improved chest contour and symmetry. Each plan is individualised following thorough assessment and discussion, ensuring that surgical precision aligns with the patient’s aesthetic goals in a safe and professional manner.
 Google Review
Google Review
 Facebook Review
Facebook Review
 Google Review
Google Review
 Google Review
Google Review
 Google Review
Google Review